
In our digital age, protecting your devices and personal information from malware is crucial. Malware, short for “malicious software,” encompasses a range of harmful programs designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Understanding the different types of malware and how they operate is key to defending yourself against these cyber threats.
Table of Contents
What is Malware?

Malware is a broad term used to describe any software designed to harm, exploit, or otherwise compromise the functionality of a computer system, network, or device. The word “malware” is derived from “malicious software,” and it encompasses a variety of hostile or intrusive software.
Key Characteristics of Malware
Malicious Intent: Malware is created with the intent to cause damage, steal information, or disrupt services.
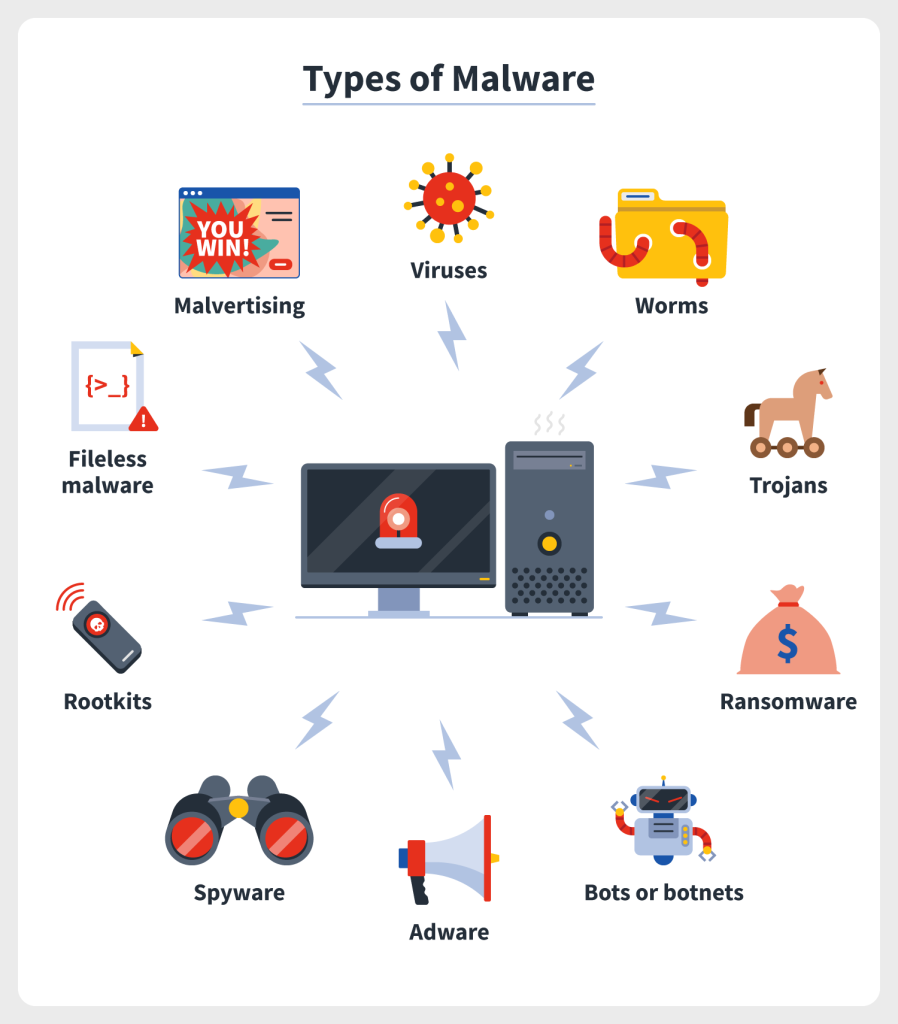
Variety: Malware comes in many forms, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and more.
Propagation: It can spread in various ways, such as through infected email attachments, malicious websites, software downloads, or network vulnerabilities.
Concealment: Many types of malware are designed to remain hidden from detection, making them difficult to identify and remove.
Viruses
Description:
A virus is one of the most well-known types of malware. It attaches itself to legitimate programs or files and spreads from one computer to another as users share infected files.
How it Spreads:
Viruses can spread through email attachments, downloads from infected websites, or via USB drives. Once activated, they can replicate themselves and infect other files and systems.
Protection Tips:
- Use reliable antivirus software and keep it updated.
- Avoid downloading attachments from unknown or suspicious emails.
- Regularly update your operating system and applications.
Worms Malware
Description:
Worms are similar to viruses but can spread without any user action. They replicate themselves and often exploit vulnerabilities in software or operating systems to spread across networks.
How it Spreads:
Worms can spread through network connections, email attachments, or by exploiting security flaws in software. They can cause widespread damage quickly.
Protection Tips:
- Keep your system and software up to date with the latest patches.
- Use firewalls to block unauthorized access.
- Regularly scan your system with anti-malware tools.
Trojans Malware
Description:
Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software but contain malicious code. Unlike viruses and worms, they do not self-replicate.
How it Spreads:
Trojans are often spread through seemingly harmless software downloads, email attachments, or websites. Once installed, they can open backdoors for hackers.
Protection Tips:
- Be cautious when downloading software from the internet.
- Verify the source and legitimacy of software before installation.
- Use anti-malware software to detect and remove Trojans.
Ransomware
Description:
Ransomware encrypts a victim’s files or locks them out of their system, demanding a ransom to restore access. It has become one of the most financially damaging types of malware.
How it Spreads:
Ransomware often spreads through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploit kits on compromised websites.
Protection Tips:
- Regularly back up important data to an external device or cloud service.
- Be vigilant about email attachments and links from unknown sources.
- Keep your security software up to date.
Spyware
Description:
Spyware secretly monitors and collects information about a user’s activities without their knowledge. It can track keystrokes, capture screenshots, and gather personal information.
How it Spreads:
Spyware can be installed through malicious downloads, software bundles, or vulnerabilities in web browsers.
Protection Tips:
- Use anti-spyware software to detect and remove spyware.
- Adjust browser settings to block pop-ups and malicious sites.
- Avoid downloading software from untrusted sources.
Adware
Description:
Adware displays unwanted advertisements on your computer. While not always malicious, it can degrade system performance and lead to more serious threats.
How it Spreads:
Adware often comes bundled with free software or downloads from the internet.
Protection Tips:
- Be cautious when installing free software; read the terms and conditions.
- Use ad-blockers and anti-adware tools.
- Regularly scan your system for unwanted programs.
Rootkits
Description:
Rootkits are designed to hide the existence of certain processes or programs from normal detection methods, allowing attackers to maintain access to a system.

How it Spreads:
Rootkits can be installed through various means, including phishing attacks, software vulnerabilities, or direct access by an attacker.
Protection Tips:
- Keep your operating system and software updated.
- Use rootkit detection tools.
- Avoid running unknown or suspicious programs with administrative privileges.
Keyloggers
Description:
Keyloggers record every keystroke made on a computer, capturing sensitive information such as passwords and credit card numbers.
How it Spreads:
Keyloggers can be installed through email attachments, software downloads, or physical access to the device.
Protection Tips:
- Use virtual keyboards for sensitive transactions.
- Install anti-keylogger software.
- Be cautious of suspicious emails and downloads.
Bots and Botnets
Description:
A bot is a type of malware that allows attackers to take control of an infected computer. A botnet is a network of such compromised computers, often used to launch large-scale attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
How it Spreads:
Bots spread through vulnerabilities in software, malicious downloads, or network connections.
Protection Tips:
- Use firewalls to block unauthorized access.
- Keep your system and applications updated.
- Regularly scan your system with anti-malware software.
Phishing
Description:
While not a malware itself, phishing is a method used to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Attackers often use fake emails or websites that look legitimate.
How it Spreads:
Phishing attacks typically come through email, but they can also occur via text messages, social media, or malicious websites.
Protection Tips:
- Be cautious of emails asking for personal information.
- Verify the authenticity of websites before entering sensitive information.
- Use email filters to block phishing attempts.

Conclusion
Understanding the different types is the first step in protecting yourself from cyber threats. By staying informed and adopting good security practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to malware attacks. Here are some general tips to help you stay safe:
- Keep your software and operating system updated.
- Use strong, unique passwords for your accounts.
- Be cautious of email attachments and links from unknown sources.
- Regularly back up your data.
- Use comprehensive security software, including antivirus and anti-malware tools.
- Educate yourself about the latest threats and how to recognize them.
Staying vigilant and proactive can go a long way in safeguarding your digital life from the ever-evolving world of malware.





