
A 403 Forbidden Error occurs when a web server forbids you from accessing the page you’re trying to open in your browser. Most of the time, there’s not much you can do. But sometimes, the problem might be on your end. Here are some things you can try.

Table of Contents
What Is a 403 Forbidden Error?
A 403 Forbidden error is an HTTP status code that indicates that the server understood the client’s request, but it refuses to authorize access to the requested resource. In simpler terms, it means that the server received the request from the user, but the server is denying access to the particular webpage or resource specified in the request.
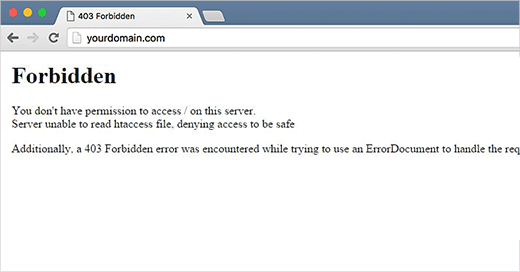
The server responds with a 403 status code to inform the client that access is forbidden, and it does not provide any additional details about why the request was denied. This lack of information is intentional to prevent disclosing sensitive details that could be exploited by malicious users.
You usually get this error for one of two reasons. The first is that the owners of the webserver have properly set up access permissions and that you’re really not allowed access to the resource. The second reason is that the owners of the webserver have improperly set up permissions and you’re getting denied access when you really shouldn’t be.
Common 403 Error Messages
Like with other errors, webmasters can customize how the 403 error is displayed. Its contents also depend on the web server used. That is why there are many different 403 pages across different websites.
Some common 403 error messages are:

- 403 Forbidden
- HTTP 403
- Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403.14 – Forbidden
- Error 403
- Forbidden: You don’t have permission to access [directory] on this server
- Error 403 – Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden Error
- 403 Error
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error
A 403 Forbidden error can occur for various reasons, and pinpointing the exact cause often requires examining server configurations, permissions, and other factors. Here are some common causes of a 403 Forbidden error:
- No index Page : In the website, there is no valid index file
- Insufficient Permissions: The most common cause is that the user making the request does not have the necessary permissions to access the requested resource. This could be due to file or directory permissions on the server.
- Authentication Issues: If the resource requires authentication, and the user hasn’t provided valid credentials or hasn’t logged in, the server may respond with a 403 error.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF) Rules: Security mechanisms like WAFs may block requests based on predefined rules. If the server thinks the request is potentially malicious or violates security policies, it may return a 403 response.
- Misconfigured Server: Server misconfigurations, including improper setup of access controls or incorrectly configured security settings, can lead to a 403 error.
- Content Protection Systems: Certain content protection systems or Digital Rights Management (DRM) mechanisms may prevent access to specific content, triggering a 403 Forbidden response.
When troubleshooting a 403 Forbidden error, administrators often need to review server logs, examine configurations, and consider the specific context of the request to determine the root cause and implement the necessary changes to resolve the issue.
How to Fix the 403 Forbidden Error
Fixing a 403 Forbidden error involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause. Here are some general steps you can take to resolve the issue:
Check URL and Permissions
- Ensure that the URL is correct and points to a valid resource.
- Verify that the user has the necessary permissions to access the resource. Check file and directory permissions on the server.
Authentication
- If the resource requires authentication, make sure the user is providing valid credentials.
- Check if the authentication mechanism is correctly configured.
Clear History/Cache
Web browsers store cached webpages to speed up loading times upon revisiting them. Occasionally, if a website link undergoes updates, the cached version may differ from the current link, leading to a 403 error when attempting to load the outdated version.
Moreover, the presence of stored cookies in your browser can contribute to the 403 error. Invalid or corrupted cookies may disrupt proper server authentication. To rectify this issue, clearing both browser cache and cookies is recommended.
Directory Listing
- If directory listing is disabled, make sure there is a default page (e.g., index.html) in the directory.
- Enable directory listing if needed, or configure a default page.
Server Misconfigurations
- Review server configurations, including access controls and security settings.
- Correct any misconfigurations that might be causing the 403 error.
Contact Server Administrator or Hosting Provider
If you’re unable to resolve the issue, contact the server administrator or hosting provider for assistance. They may provide insights or make necessary adjustments.
Remember that the specific steps may vary based on the server type (e.g., Apache, Nginx) and the web application framework in use. Always check server logs for more detailed error messages, as they can provide valuable information about the root cause of the 403 Forbidden error.
Conclusion
Ensuring high website availability is essential for delivering an optimal user experience and establishing reliability. Consequently, website owners prioritize maintaining continuous access to their sites and invest in services dedicated to website upkeep. Effectively preventing or swiftly addressing HTTP errors is pivotal for retaining your site visitors. Following this guide, you should acquire the knowledge to promptly resolve the 403 Forbidden error, thereby sustaining the seamless operation of your business.





